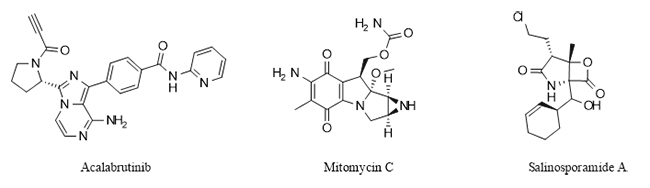
Figure 1 Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic drugs
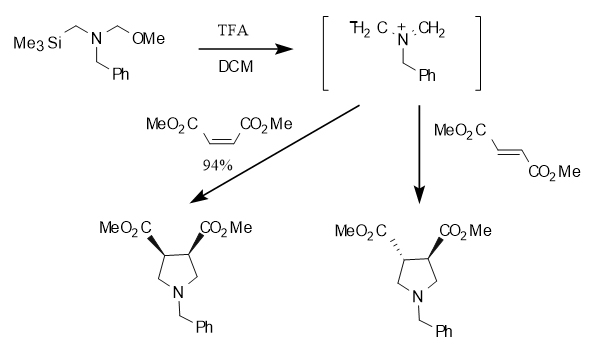
There are many methods for synthesizing nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds, including cycloaddition reactions, chemical enzymatic synthesis, asymmetric catalysis, organic electrosynthesis, etc. Among them, cycloaddition reactions are commonly used to construct such compounds. N-(Methoxymethyl)-N-(trimethylsilylmethyl)benzylamine is a 1,3-dipole that can generate a methyleneamine-type ylide in situ under the action of catalysts such as trifluoroacetic acid and TBAF, and then undergo a [3+2] cycloaddition reaction with a dipolephile to obtain a five-membered nitrogen heterocyclic compound. It is worth mentioning that the reaction exhibits complete cis stereoselectivity with chain olefins, which means that the original relative stereo configuration of the molecule is maintained during the reaction. This feature is of great significance for synthesizing complex molecules with specific spatial structures. As shown in Figure 2 below
Figure 2 Cycloaddition reaction with chain olefins
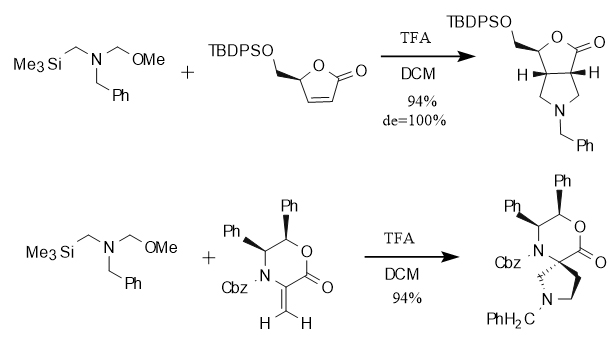
In addition, in the [3+2] cycloaddition reaction involving N-(methoxymethyl)-N-(trimethylsilylmethyl)benzylamine, excellent diastereoselectivity is shown when reacting with olefins containing cyclic structures. This property is crucial for constructing molecules with complex spatial configurations. Specifically, when reacting with cycloolefins (double bonds in the ring), fused ring compounds are generated, while when reacting with double bonds outside the ring (connected to the ring), spiro compounds are generated. This reaction characteristic can selectively construct specific types of cyclic structures, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Cycloaddition reaction with cyclic olefins
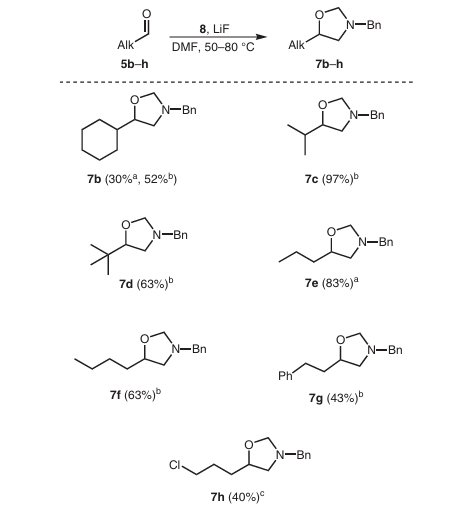
It is worth mentioning that the methylene amine-type ylide formed by N-(methoxymethyl)-N-(trimethylsilyl methyl)benzylamine can not only react with carbon-carbon double bonds to form rings but also react with carbonyl groups A cycloaddition reaction occurs to prepare oxazolidine compounds, as shown in Figure 4: under the catalysis of lithium fluoride, N-(methoxymethyl)-N-(trimethylsilyl methyl)benzylamine reacts with different types of The reaction of fatty aldehydes yields the corresponding oxazolidine compounds in good yields.
Figure 4 Cycloaddition reaction with aliphatic aldehydes
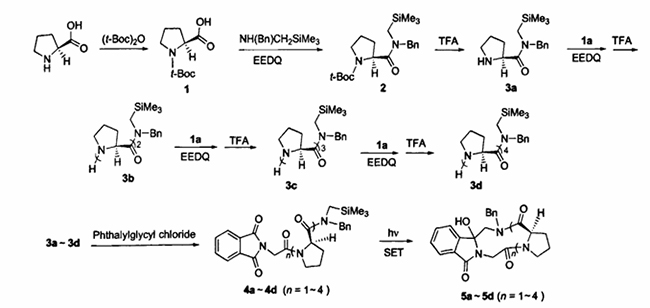
N-(Methoxymethyl)-N-(trimethylsilylmethyl)benzylamine is a commonly used reagent in cycloaddition reactions and is widely used in the synthesis of polysubstituted pyrrolidine compounds and pharmaceutical intermediates. This compound is usually obtained by reacting N-(trimethylsilylmethyl)benzylamine with formaldehyde and methanol. The raw material N-(trimethylsilylmethyl)benzylamine is also an important organic synthesis intermediate. It can react with reagents such as aldehydes to directly construct heterocyclic compounds through three-component reactions. It can also be used to synthesize nitrogen heterocyclic proline peptides, as shown in Figure 5:
Figure 5 Synthesis route of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic proline peptides
References
[1] Amin, A.; Qadir, T.; Abe, H.; et al. A Review on The Medicinal And Industrial Applications of N-containing heterocycles [J]. The Open Medicinal Chemistry Journal, 2022, 16.
[2] Kumar, A.; Singh, AK; Kumar, P.; et al. Nitrogen-Containing Heterocycles as Anticancer Agents: AMedicinal Chemistry Perspective[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2023, 16, 299.
[3] N-Benzyl-N-(methoxymethyl)-N-trimethylsilylmethylamine. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2001.
[4] Gorbunova, E.; Buev, EM; Moshkin, VS; et al. Three Ways Aliphatic Aldehydes React with Nonstabilized Azome Thine Ylides[J]. SynLett, 2020, 31.
[5] Liu Yan, Tan Guanghui, Jin Yingxue et al. Synthesis of N-heterocyclic Proline Peptides by Photoinduced Single Electron Transfer Reaction[J]. Organic Chemistry, 2011, 31, 480-485.